2.- SIP User Agents
User Agents
A SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) user agent is a software application that runs on a device and communicates with other devices using the SIP protocol. A user agent can act as a client, a server, or both.
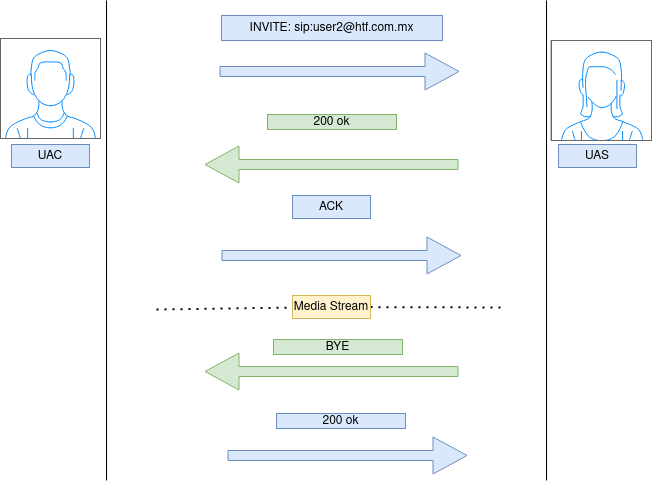
There are two types of SIP user agents: User Agent Client (UAC) and User Agent Server (UAS).
A User Agent Client (UAC) is a SIP endpoint that initiates a SIP session. The UAC sends SIP requests to other SIP user agents, such as a User Agent Server (UAS), to establish a session. The UAC is responsible for generating the SIP requests, processing responses, and terminating the session.
A User Agent Server (UAS) is a SIP endpoint that responds to SIP requests. When a UAS receives a SIP request, it generates a SIP response that is sent back to the requesting user agent. The UAS is responsible for processing the SIP requests, generating the SIP responses, and maintaining the session.
Both UAC and UAS can be implemented as separate software applications or combined into a single application. For example, a softphone application can act as both a UAC and a UAS, allowing users to initiate and receive calls using SIP.
In addition to UACs and UASs, there are other types of SIP user agents, such as a Proxy Server, which forwards SIP messages between user agents, and a Redirect Server, which redirects SIP messages to other servers or user agents.
No Comments