18. - SIP - Firewall NAT and SBC
- Firewalls
- NAT & Types of NAT
- Firewall / NAT solutions
- THE RTP Problem
- MG, ALG, SBC
Issues to Address
Protection of your network is vital if connected to the internet, Private addressing on the internal network can cause problems when using SIP through a NAT (network address translation service), NAPT also introduces another set of problems and finally SIP has a firewall to content with.
Firewalls
Corporate and personal firewalls are usually placed at the wedge of the network to act as a perimeter device that can permit traffic leaving and entering thenetwork, usually all traffic originating from within a network is allowed out and traffic from outside is allowed in, firewalls usually allow traffic such as HTTP and SMTP to enter the network, firewalls that are not SIP aware will probably block all SIP traffic and it may be the case that the RTP packets will be blocked as well.
NAT
Private addressing on the internal network can cause problems wueh using SIP through a NAT
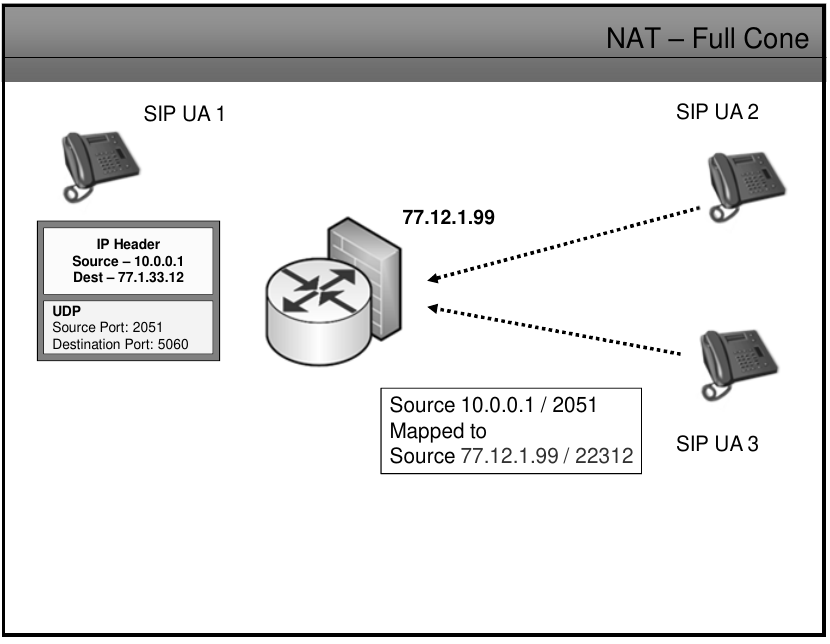
Full-cone NAT
- Once an internal address (iAddr:iPort) is mapped to an external address (eAddr:ePort), any packets from iAddr:iPort will be sent through eAddr:ePort.
- Any external host can send packets to iAddr:iPort by sending packets to eAddr:ePort.
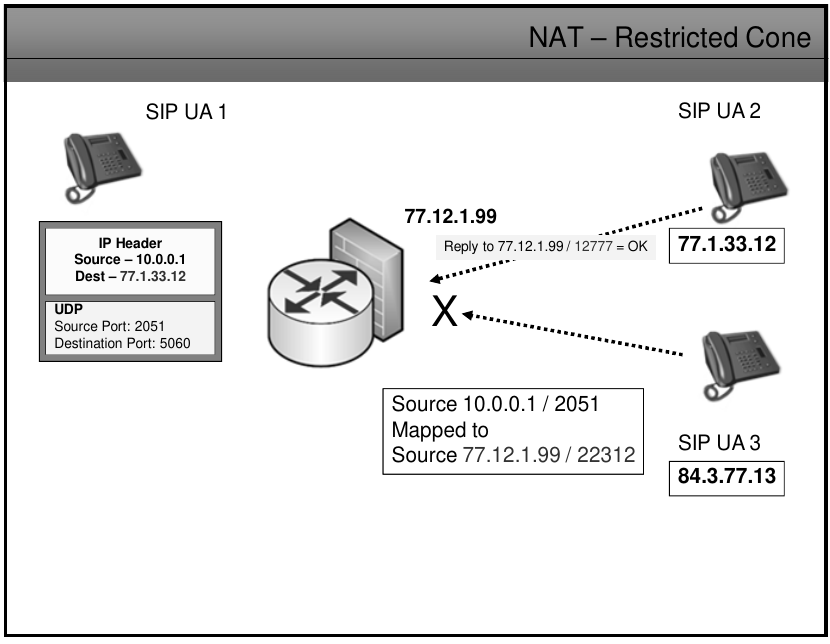
Restricted Cone NAT
- Once an internal address iAddr:iPort is mapped to an external address eAddr:ePort, any packets from iAddr:iPort will be sent through eAddr:ePort
- An External host hAddr:any can send packets to iAddr:iPort by sending packets to eAddr:ePort only if iAddr:iPort has previously sent a packet to hAddr:any. "ANY" means the port number doesn't matter.
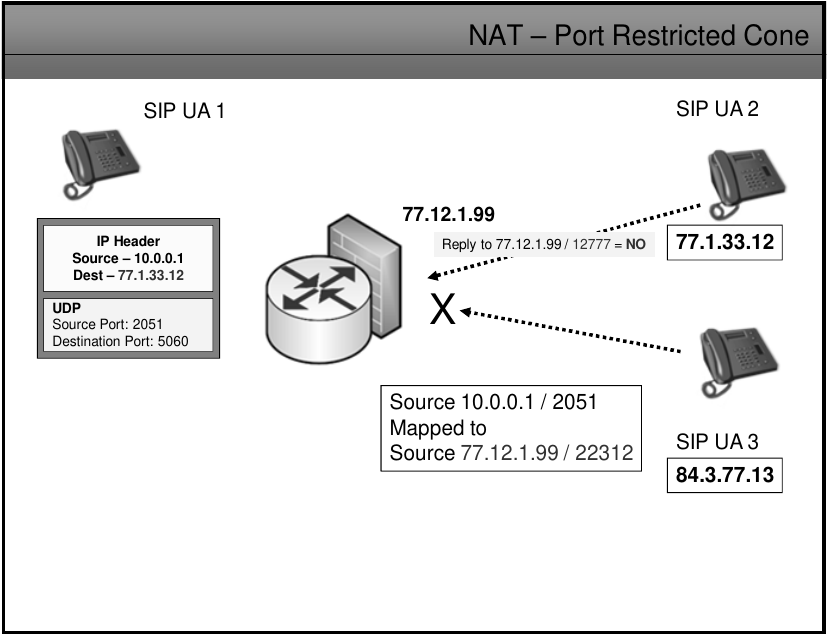
Port Restricted NAT
- Like an address restricted cone NAT, but the restriction includes port numbers.
- Once and internal address iAddr:iPort is mapped to an external address eAddr:ePort, any packets from iAddr:iPort will be sent through eAddr:ePort.
- An external host hAddr:hPort can send packets to iAddr:iPort by sending packets to eAddr:ePort only if iAddr:iPort has previously sent a packet to hAddr:hPort.
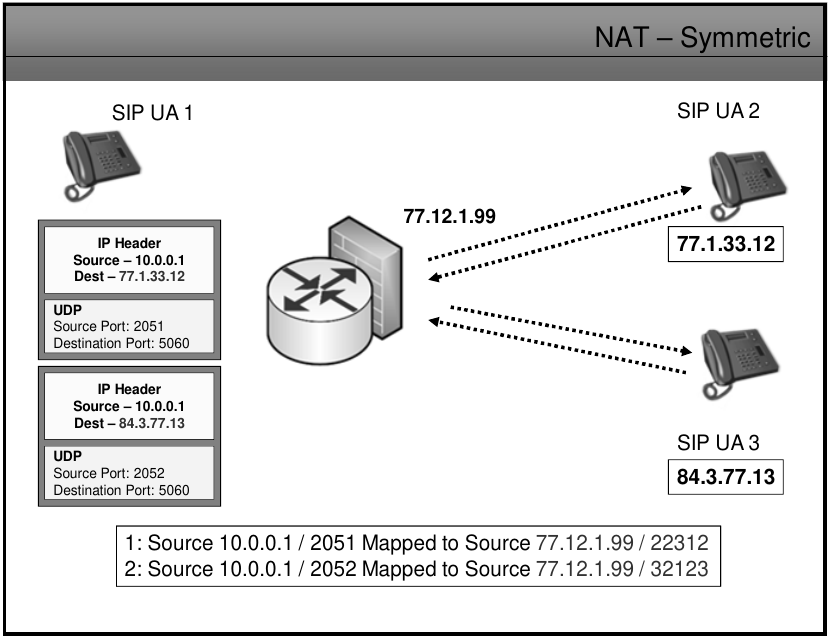
NAT Symmetric
- Each request from the same internal IP address and port to a specific destination IP address and port is mapped to a unique external source IP address and port, if the same internal host sends a packet eeven with the same source address and port but to a different destination a different mapping is used.
- Only an external host that receivs a packet from an internal host can sed a packet back.
NAPT Introduces another set of problems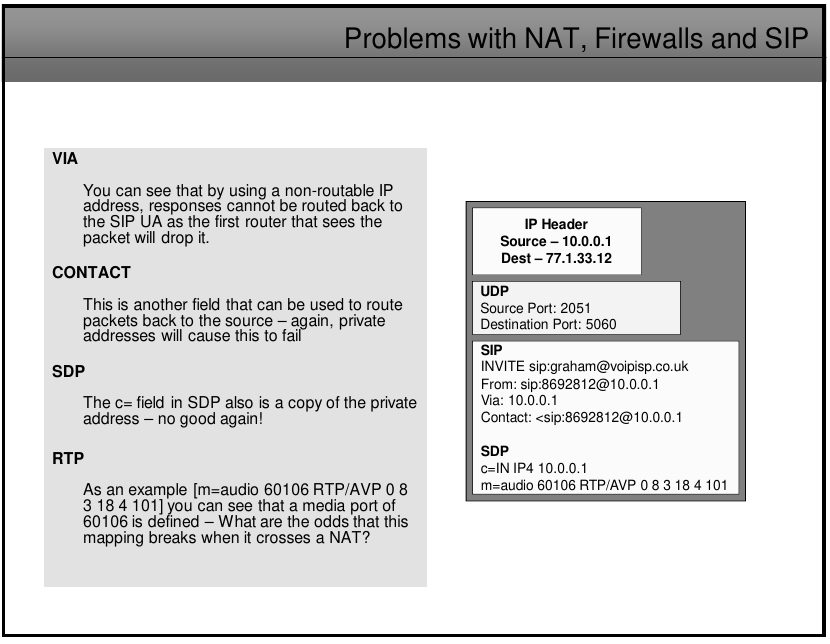
Problems with NAT are caused because of the hostile environment made for the lack of standardize behaviors and controls in NATs solutions.
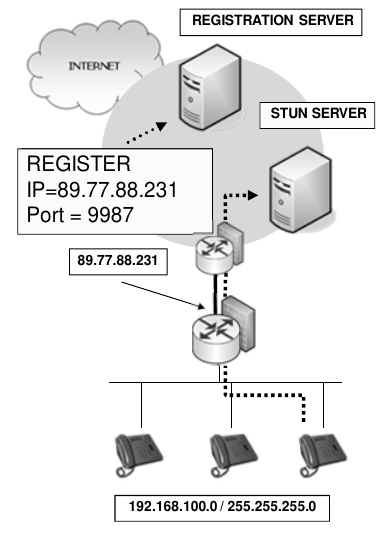
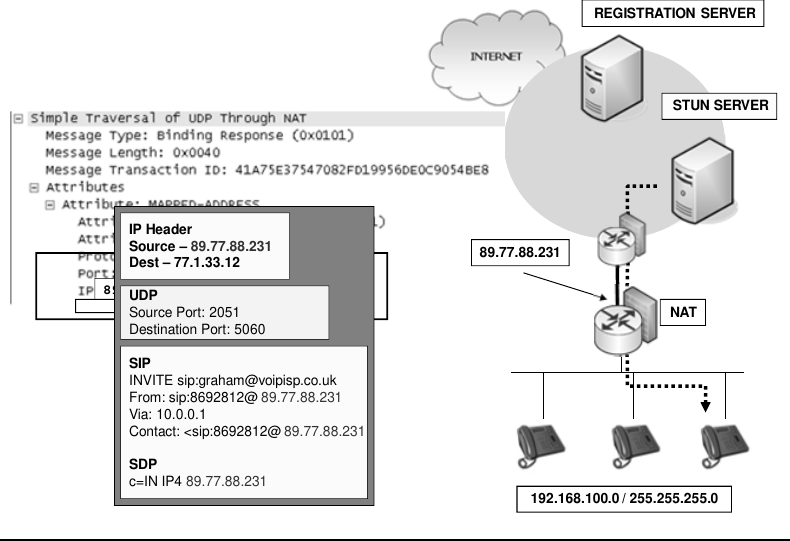
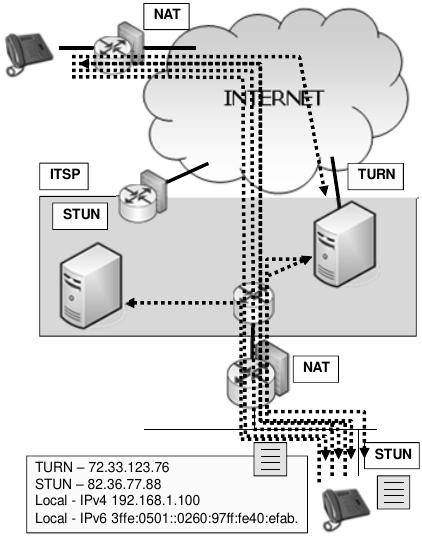
STUN (Simple Transversal of UDP)
How it works
- Allow to communicate across NATs before making calls client contacts STUN SERVER to find out the external IP address that is using, on port 3489, that way when seeding the messages clients can get back to the originating client.
- Also use port IP/Port details in its register to the registration server to keep the appropriate firewalls port open.
- Rport entry overrides the dst port when SIP messages are returned to the client behind NAT as it is what STUN can see.
- Rport is filled in by the proxy or UAS.
Problems
- STUN doesnt work behind symmetric NAT as the new IP/Port mappings are created for each session
- if firewalls are configured to drop UDP packets it will fail
- UDP is not connection oriented so firewalls may close port pinholes causing session to fail
- Multiple NAT can have problems

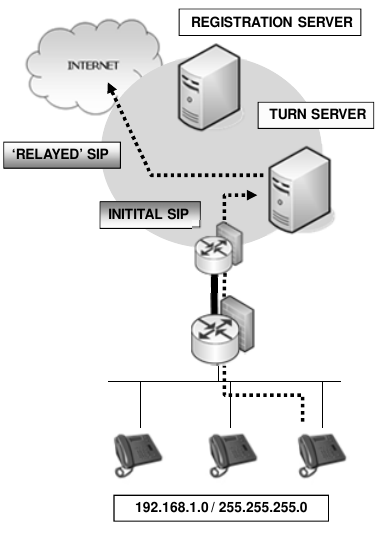
TURN (Traversal Using Relays around NAT)
- Operates similar to STUN but it can also relay RTP streams as well as SIP messages (both are proxied)
- Works with both UDP and TCP so TCP can be used to ensure session stay open
- TURN works with symmetric NAT
- TURN must have an internet facing address
Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE)
- ICE UA make a series of connectivity check in order to discover which is the set of IP address that will be guaranteed to work
- Loos at all of its local addresses and then queries its STUN and TURN server to collect more addresses it can be reached.
- Then it starts its own STUN service, passes a copy of the IP addresses to it and then sends all of the collected IP address to the destination device
- The destination responds by sending a STUN request to each IP address with initiates a STUn reply back to the destination client with details of each IP address that worked
- The STUN deevice then sends a final notification back to the destination device to confirm the connection details
- ICE RFC 5245
- Will take time to enable ICEE clients, good news is that actual devices may only need software upgrade or patch
- Due to chaotic implementation of NATs it could take a while to implement ICE
- AS it checks for the bes IP/Port combination to usee it delays the call setup time.
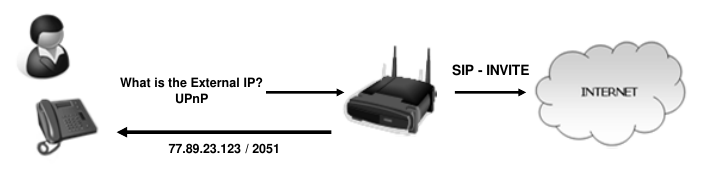
UPnP
- The protocol running on the SIP devices queries the firewall/NAT directly for the external public address and port numbers
- SIP device rewrites private addresses as usual in the sip message and SDP body with the public address
- UpnP is supported by the majority of manufacturers
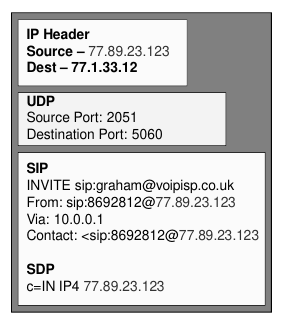
RTP Problem
- When caller inside send the rtp packet the firewall cannot know which port is going to bee used so the response can be blocked
- When caller outside send the rtp packet the firewall cannot know which port is being used for audio so the response can be blocked
Solving the RTP problem
- RTP are dynamically allocated
- Firewall don't know these details
- Opening more firewall ports is not an option
- Symmetric RTP
- The audio is sent to the port used for signaling as it is already opened
- Media Proxy
- The SIP device register in the media proxy and forward the registration to the registration server as it was the SIP device.
- ALG (Application level gateway)
- Is not unlike a MEdia Proxy
- Can sit inside a DMZ controlled by the firewall
- All sip and rtp packets are sent to the ALG
- Works with NAT by changing the SDP body of the SIP
- Can be software that is embedded on the firewall
- SIP Aware Firewall
- Rewrites the ports used to send the audio
- SBC
- Control billing
- Ensure QoS
- Apply usage policies
- Apply security policies
- Firewall/NAT issues
- SBC Enterprise
- Act as an ALG
- Codec conversion
- TLS, SRTP and/or IPSec
- Reemote SIP devices
- Benefits
- Hide ip addressing
- Apply CAC
- Apply Security policies
- Apply QoS settings
- Billing Services
- Scalatee to 100,000 connections
No Comments