Install terraform in docker container
On Debian
Ensure that your system is up to date and you have installed the gnupg, software-properties-common, and curl packages installed. You will use these packages to verify HashiCorp's GPG signature and install HashiCorp's Debian package repository.
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y gnupg software-properties-commonInstall the HashiCorp GPG key.
$ wget -O- https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com/gpg | \gpg --dearmor | \sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg > /dev/nullVerify the key's fingerprint.
$ gpg --no-default-keyring \--keyring /usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg \--fingerprintThe gpg command will report the key fingerprint:
/usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg
-------------------------------------------------
pub rsa4096 2023-01-10 [SC] [expires: 2028-01-09]
798A EC65 4E5C 1542 8C8E 42EE AA16 FCBC A621 E701
uid [ unknown] HashiCorp Security (HashiCorp Package Signing) <[email protected]>
sub rsa4096 2023-01-10 [S] [expires: 2028-01-09]Refer to the Official Packaging Guide for the latest public signing key. You can also verify the key on Security at HashiCorp under Linux Package Checksum Verification.
Add the official HashiCorp repository to your system. The lsb_release -cs command finds the distribution release codename for your current system, such as buster, groovy, or sid.
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg] \https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com $(lsb_release -cs) main" | \sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/hashicorp.listDownload the package information from HashiCorp.
$ sudo apt updateInstall Terraform from the new repository.
$ sudo apt-get install terraformIf you use either Bash or Zsh, you can enable tab completion for Terraform commands. To enable autocomplete, first ensure that a config file exists for your chosen shell.
$ touch ~/.bashrcThen install the autocomplete package.
$ terraform -install-autocompleteOnce the autocomplete support is installed, you will need to restart your shell.
Now that you've installed Terraform, you can provision an NGINX server in less than a minute using Docker on Mac, Windows, or Linux. You can also follow the rest of this tutorial in your web browser.
Click on the tab(s) below relevant to your operating system.
To follow this tutorial on Linux, first install Docker Engine for your distribution.
Create a directory named learn-terraform-docker-container.
$ mkdir learn-terraform-docker-containerThis working directory houses the configuration files that you write to describe the infrastructure you want Terraform to create and manage. When you initialize and apply the configuration here, Terraform uses this directory to store required plugins, modules (pre-written configurations), and information about the real infrastructure it created.
$ cd learn-terraform-docker-containerIn the working directory, create a file called main.tf and paste the following Terraform configuration into it.
terraform { required_providers { docker = { source = "kreuzwerker/docker" version = "~> 3.0.1" } }}provider "docker" {}resource "docker_image" "nginx" { name = "nginx" keep_locally = false}resource "docker_container" "nginx" { image = docker_image.nginx.image_id name = "tutorial" ports { internal = 80 external = 8000 }}Initialize the project, which downloads a plugin called a provider that lets Terraform interact with Docker.
$ terraform initterraform init
root@dockerpx:/home/dockers/terraform# terraform init
Initializing the backend...
Initializing provider plugins...
- Finding kreuzwerker/docker versions matching "~> 3.0.1"...
- Installing kreuzwerker/docker v3.0.2...
- Installed kreuzwerker/docker v3.0.2 (self-signed, key ID BD080C4571C6104C)
Partner and community providers are signed by their developers.
If you'd like to know more about provider signing, you can read about it here:
https://www.terraform.io/docs/cli/plugins/signing.html
Terraform has created a lock file .terraform.lock.hcl to record the provider
selections it made above. Include this file in your version control repository
so that Terraform can guarantee to make the same selections by default when
you run "terraform init" in the future.
Terraform has been successfully initialized!
You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see
any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands
should now work.
If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform,
rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other
commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
Provision the NGINX server container with apply. When Terraform asks you to confirm type yes and press ENTER.
$ terraform applyVerify the existence of the NGINX container by visiting localhost:8000 in your web browser or running docker ps to see the container.
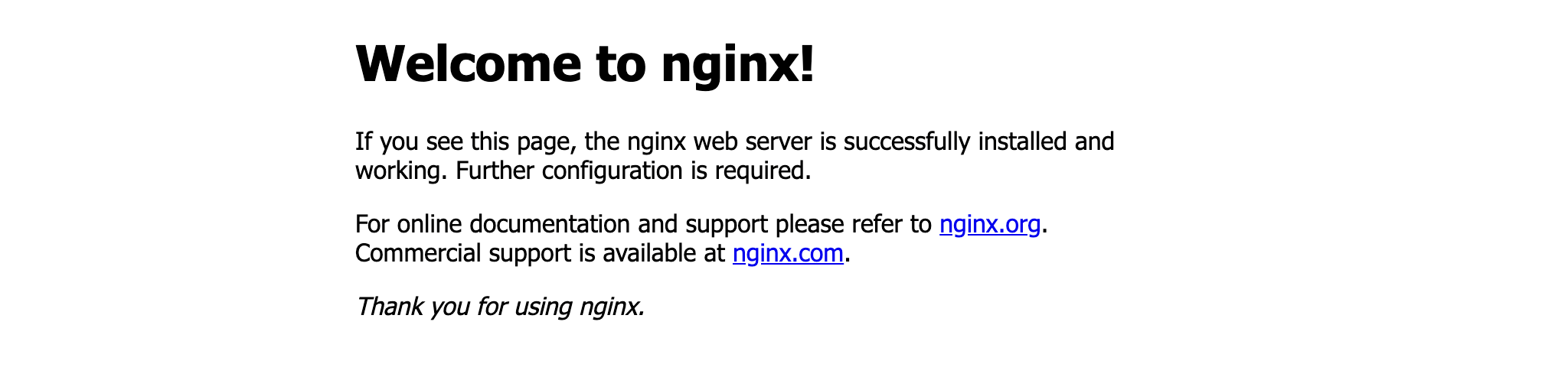
$ docker psCONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES425d5ee58619 e791337790a6 "nginx -g 'daemon of…" 20 seconds ago Up 19 seconds 0.0.0.0:8000->80/tcp tutorialTo stop the container, run terraform destroy.
$ terraform destroyYou've now provisioned and destroyed an NGINX webserver with Terraform.